The link between Food Hygiene Ratings and Deprivation

Introduction
If you’ve ever visited any food establishment in England & Wales, you’ve probably noticed the green labels somewhere on the outside with a Food Hygiene Rating from 0-5 on it. If you haven’t, then put simply - every food establishment in England / Wales is required to have a food hygiene inspection, and on the basis of this inspection is rated on a scale of 0-5, with 5 being “crack on, enjoy your dinner”, and 0 being “hmm, maybe don’t risk it”. I explored these Food Hygiene Ratings for my Masters’ dissertation with the overarching question:
Are the ratings randomly scattered around the country and if they are not, what are some of the variables that influence this?
How are Food Hygiene Ratings calculated?
So, how do the inspectors quantify an inspection and how are Food Hygiene Ratings calculated? During an inspection, the establishment is marked on three criteria:
- Hygiene: how well the food is being stored, prepared and cooked;
- Structural: the layout of the premises - inspectors are looking for cleanliness, ventilation and pest control; and
- Management: the standard of the paperwork and training - how confident the inspectors are that the standards seen will be maintained after the inspection.
They are then given a score in each of the three categories. These scores are added together to produce an Overall Score, which is then mapped to a Food Hygiene Rating.
The Data
To answer the first half of our question, we need to know the scores for all of the food establishments in the country. Thankfully, the Food Standards Agency, the organisation which oversees the inspections, maintains an up-to-date database which contains all the information required. They even have a section of their website dedicated to helping users call API’s.
For the second half of our question, we decided to investigate whether the Food Hygiene Ratings vary depending on how deprived an area is. Deprivation data is available for all four nations of the UK (England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales) but each country compiles its own. This means that the data is not comparable - the most deprived local area in England is not necessarily equivalent to the most deprived local area in Wales. As a result of this, we only used establishments in England in the project.
Reproducible - shown at the bottom.
Data Exploration
Let’s start by taking a look at how many establishments have each rating:
Around ~75% of establishments obtain a rating of 5. This is great for dinner, but not so great for data analysis, as there isn’t much to differentiate between establishments. It might also be helpful to know the different types of establishments, and how many there are in each category:
| Type of Establishment | Count |
|---|---|
| Restaurant/Cafe/Canteen | 94494 |
| Retailers - other | 68864 |
| Takeaway/sandwich shop | 44631 |
| Other catering premises | 42954 |
| Pub/bar/nightclub | 41004 |
| Caring Premises | 31736 |
| School/college/university | 25742 |
| Mobile caterer | 17404 |
| Hotel/bed & breakfast/guest house | 12440 |
| Retailers - supermarkets/hypermarkets | 11237 |
| Manufacturers/packers | 4845 |
| Distributors/Transporters | 1194 |
| Farmers/growers | 478 |
| Importers/Exporters | 178 |
Visualising the Data
We’re interested in whether Food Hygiene Ratings are randomly scattered across the country, so it would be useful to view the data as a map. However, looking at the numbers of establishments above, it’s very clear that it is neither useful nor feasible to plot every single establishment individually - we would just be colouring in a map of England. We need some way of grouping the data, and while there are obviously a number of different ways to do this, we chose to use postcode districts.
In the UK, most postcodes are of the form LLNN NLL (where L denotes a Letter, N a number). The first group of letters indicate the postcode area and are normally fairly intuitive. For example, all postcodes in the NEwcastle upon Tyne area start with NE. The first group of numbers indicate the postcode district. For example, the city centre of Newcastle upon Tyne is NE1.
By extracting both the postcode area and postcode district from the full postcode we were able to group establishments by postcode district and then simply calculate the mean of the Ratings.
The associated postcode shapefiles are available on GitHub. Importing these into R and merging with the postcode district values, gives us a nice data set that we could then plot onto a map. Using {leaflet}, we generated the following choropleth map.
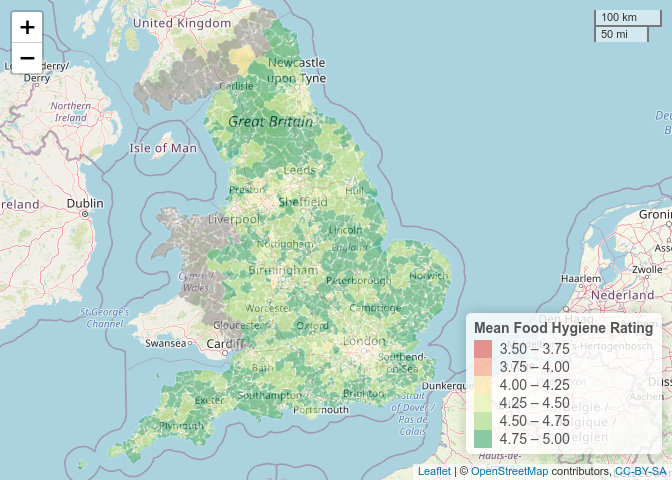
It looks like the areas of lower ratings seem to coincide with city centres/urban areas (look at London, Manchester, Birmingham, Liverpool, Newcastle - these areas are considerably more “yellowy-red” than other areas). We can probably come up with many reasons why this might be the case. One possibility is that city centres may attract different types of establishments than rural areas which then in turn are linked to having lower ratings - city centre takeaways probably score lower than countryside guest houses. Another possibility is deprivation data is playing some part in the geographical spread of ratings; 12% of people living in urban areas live in an area that is in the top 10% most deprived areas, this drops to only 1% of people when we consider rural areas. This seems worth investigating.
Modelling with Deprivation Data
To investigate this potential link, we needed to implement regression techniques, meaning that we needed to create a data set with establishments and their corresponding deprivation data. Deprivation data is collated and made available fairly regularly; we used the data published in 2019. England is split up into small areas called LSOAs for purposes such as the census and deprivation data. There are 32,844 LSOAs in England and each LSOA is given a deprivation score which is made up from seven different factors:
- Income Deprivation
- Employment Deprivation
- Education, Skills and Training Deprivation
- Health Deprivation and Disability
- Crime
- Barriers to Housing and Services
- Living Environment Deprivation
In each of the seven criteria, LSOAs are given higher scores for performing worse. The most deprived LSOA in England is Tendring, Essex with a score of 92.735 and the least deprived LSOA in England is Chiltern, Buckinghamshire with a score of 0.541.
We can combine the deprivation and the food hygiene data via their postcode. Using ordinal regression, we can model the relationship between deprivation data and ratings:
estDepMerged = readRDS("data/estDepMerged.rds")
model = MASS::polr(formula = factor(rating) ~ `Index of Multiple Deprivation (IMD) Score`,
data = estDepMerged)
model
# Call:
# MASS::polr(formula = factor(rating) ~ `Index of Multiple Deprivation (IMD) Score`,
# data = estDepMerged)
#
# Coefficients:
# `Index of Multiple Deprivation (IMD) Score`
# -0.01185
#
# Intercepts:
# 0|1 1|2 2|3 3|4 4|5
# -6.911 -4.417 -3.671 -2.422 -1.266
#
# Residual Deviance: 589111.36
# AIC: 589123.36
This model allows us to estimate the chance of picking a restaurant with a top hygiene rating based on the location, i.e. deprivation. For the wealthiest regions, the chances of picking an establishment with a rating of 5, is around 0.78. If we include 4’s & 5’s, this probability is raises to 0.92. For establishments on the other end of the spectrum, the probability of a rating of 5 is only 0.54. Including 4’s & 5’s increase this probability of 0.79.
Summary
Despite the overwhelming number of high food hygiene ratings (which, again, I am not complaining about as far as dinner is concerned), we were still able to see some interesting (read, concerning) patterns in the hygiene rating locations. There is a clear link between deprivation scores and food hygiene ratings, which we can see in the above percentages alongside the colour coded map - you are much more likely to encounter an establishment with a rating of five in the least deprived areas than in the most deprived.
We acknowledged earlier that there is also a difference in the type of establishment in the different locations, but perhaps this is just more of the same story? Yes there are different types of establishments in different locations, but why is that? It isn’t a huge leap to suggest that this is also related to the deprivation level of the location. In fact, when we investigated further, we found that deprived areas not only had a large number of takeaways, but these takeaways tended to score lower (on average) in terms of food hygiene.
Futher information
- All code is available at our GitHub Repo.
- This work was initially carried out by James Salsbury as part of his MMathStat project at Newcastle University. James is now a PhD student at the University of Sheffield looking at Bayesian experimental design for adaptive clinical trials.

